Joint pain and mobility- empowering elderly with arthritis
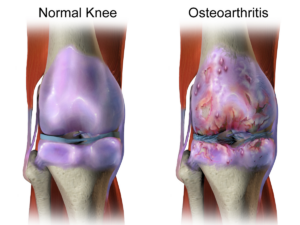
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common joint disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a degenerative disease that causes the cartilage (a form of connective tissue) in the joints to break down, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. It can affect any joint in the body and commonly occurs in the knees, hips, hands, and spine.
What causes Osteoarthritis
The exact cause of OA is unclear, but several factors can increase the risk of developing the condition. Age is an important factor, as the wear and tear on joints increase with age. Other factors that contribute to the development of OA include obesity, joint injury or overuse, genetics, and other medical conditions, like rheumatoid arthritis.
What are the symptoms of osteoarthritis
The symptoms of OA vary depending on the joint affected and the severity. The most common symptoms include pain, stiffness, and swelling, after overuse and waking up in the morning. The pain may worsen with activity and may be relieved by rest. As the disease progresses, the joint and the affected joint may make a cracking or popping sound during movement.
How osteoarthritis is diagnosed
Your physician will take a medical history of how things started and its progression. It is followed by a physical examination of the affected joint. The doctor may also order imaging tests like X-rays, to evaluate the joint’s condition and assess the extent of cartilage damage. Blood tests may also be ordered to rule out other conditions that mimic arthritis knee.
How Osteoarthritis is treated
The treatment options for OA focus on three principles.
- reducing pain and stiffness
- improving joint function
- slowing down the progression of the disease.
Some treatment options include:
Lifestyle changes
One of the most effective ways is to make lifestyle changes that reduce stress on the affected joint. For example, maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce pressure on the knees and hips. Exercise can also help strengthen the muscles and ligaments (tissues connecting bones and muscles) around the affected joint. It will help in reducing the pain and improve mobility. Low-impact exercises like swimming and cycling are also beneficial for people with OA.
Medications
Medications are given to relieve pain. It may be simple painkillers like paracetamol or a class of drugs known as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and very rarely corticosteroids. These medications can help reduce pain and inflammation in the affected joint.
Physical therapy
Physical therapy can help improve joint mobility and reduce pain by using exercises. The therapist may also use heat or cold therapy, ultrasound, or other techniques like wax, or IR to help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
Surgery
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace the affected joint. Joint replacement surgery involves removing the damaged joint and replacing it with an artificial joint made of metal and plastic.
Prevention of osteoarthritis
While there is no sure way to prevent OA, there are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing the condition. Maintaining a healthy weight, getting regular exercise, and avoiding injury or overuse of the joints can all help reduce the risk of OA. Additionally, avoiding smoking and reducing alcohol consumption may also help reduce the risk of developing OA.
Conclusion
Osteoarthritis is a common joint disorder that can cause pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Treatment options for OA focus on reducing pain and stiffness, improving joint function, and slowing down the progression of the disease. Prevention is possible by maintaining a healthy lifestyle and habits.